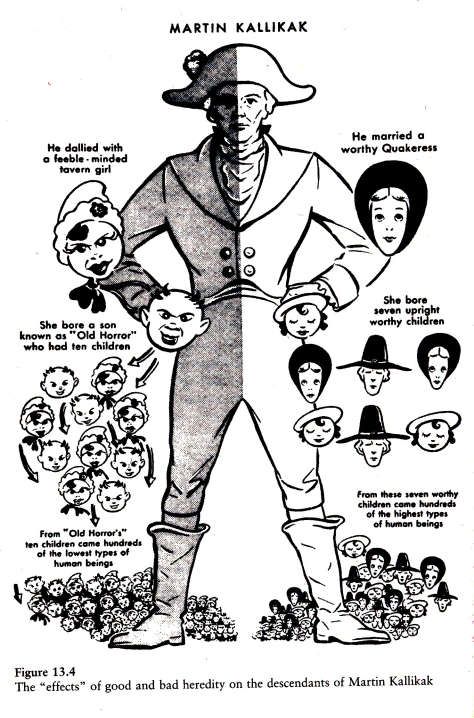
With the popularity of eugenic
theories, the segregation and institutionalization of the differently
abled and general public vilification, a fertile ground had been
prepared for what came next.
A Call for Euthanasia
Many countries followed America's eugenics movement and imitated it's legislation. In countries such as France, Belgium, Sweden, England and Germany, eugenic principles were introduced into everyday life. Many US states had passed sterilization laws, Indiana being the first in 1907.
The 1912 International Eugenics Congress featured a paper called "Preliminary Report of the Committee of the Eugenic Section of the American Breeders' Association to Study and to Report on the Best Practical Means for Cutting Off the Defective Germ-Plasm in the Human Population", in which ten solutions were put forth to deal with the "socially unfit". They were, in order: Life segregation (or segregation during the reproductive period), Sterilization, Restrictive Marriage laws and customs, Eugenic Education of the public and of prospective marriage mates, Systems of matings purporting to remove defective traits, General environmental betterment, Polygamy, Euthanasia, Neo-Malthusian doctrine, artificial interference to prevent conception and Laissez-faire. An 1918 Eugenics Textbook "Applied Eugenics" by Paul Popenoe and Roswell H. Johnson, listed many suggestions as well, among which:
Charles Davenport, author of Eugenics, The Science of Human Improvement by Better Breeding and one of the creators of the Eugenics Record Office (with funding from the estate of railroad baron E. H. Harriman) was particularly close with his German colleagues; even after America was in the grips of the Great Depression, American charities such as the Carnegie Institute and Rockefeller Foundation continued to fund German eugenics research. However, the eugenics world continued to watch closely the American "accomplishments" of "biological courts", involuntary sterilization, segregation, detention, propaganda, perpetuating of pseudo-science and the ongoing discussion of euthanasia.
In 1924, an imprisoned corporal of the German Army began to study eugenic writings, including those of Davenport, Popenoe, Leon Witney and Madison Grant, who blamed the corruption of the Nordic ideal on Jews, Slavs, Afro-Americans and many others who were not blonde or blue eyed. In his book The Passing of the Great Race or The Racial Bias of European History, Grant wrote:
The young corporal, Adolf Hitler, went on to write
fan mail to both Whitney and Grant. Hitler's letter to Grant thanked
him for his book and referred to it as "my bible". In his own book, Mein Kampf, published shortly thereafter, Hitler echoed his eugenics heroes with the following call for euthanasia:
A Call for Euthanasia
Many countries followed America's eugenics movement and imitated it's legislation. In countries such as France, Belgium, Sweden, England and Germany, eugenic principles were introduced into everyday life. Many US states had passed sterilization laws, Indiana being the first in 1907.
The 1912 International Eugenics Congress featured a paper called "Preliminary Report of the Committee of the Eugenic Section of the American Breeders' Association to Study and to Report on the Best Practical Means for Cutting Off the Defective Germ-Plasm in the Human Population", in which ten solutions were put forth to deal with the "socially unfit". They were, in order: Life segregation (or segregation during the reproductive period), Sterilization, Restrictive Marriage laws and customs, Eugenic Education of the public and of prospective marriage mates, Systems of matings purporting to remove defective traits, General environmental betterment, Polygamy, Euthanasia, Neo-Malthusian doctrine, artificial interference to prevent conception and Laissez-faire. An 1918 Eugenics Textbook "Applied Eugenics" by Paul Popenoe and Roswell H. Johnson, listed many suggestions as well, among which:
"... the first method which presents itself is execution. This has been used since the beginning of the race, very probably, although rarely with a distinct understanding of its eugenic effect; and its value in keeping up the standard of the race should not be underestimated."American eugenicists felt that American society was not ready yet to implement organized euthanasia, however many institutions and physicians within employed their own methods. Passive methods included allowing infants to starve to death (such as famed MD and wanna-be-movie star Harry J Haiselden) and withholding treatment. One large institution in Illinois however, fed it's patients tuberculosis infected milk believing that the genetically superior inmates would have immunity. That particular institution, not surprisingly, had a 30 to 40 percent death rate per year. Sterilization remained the most popular method; in the first year of California's sterilization legislation for example, 9,782 people were sterilized. Most of these were women.
Charles Davenport, author of Eugenics, The Science of Human Improvement by Better Breeding and one of the creators of the Eugenics Record Office (with funding from the estate of railroad baron E. H. Harriman) was particularly close with his German colleagues; even after America was in the grips of the Great Depression, American charities such as the Carnegie Institute and Rockefeller Foundation continued to fund German eugenics research. However, the eugenics world continued to watch closely the American "accomplishments" of "biological courts", involuntary sterilization, segregation, detention, propaganda, perpetuating of pseudo-science and the ongoing discussion of euthanasia.
In 1924, an imprisoned corporal of the German Army began to study eugenic writings, including those of Davenport, Popenoe, Leon Witney and Madison Grant, who blamed the corruption of the Nordic ideal on Jews, Slavs, Afro-Americans and many others who were not blonde or blue eyed. In his book The Passing of the Great Race or The Racial Bias of European History, Grant wrote:
"Mistaken regard for what are believed to be divine laws and a sentimental belief in the sanctity of human life, tend to prevent both the elimination of defective infants and the sterilization of such adults as are themselves of no value to the community. The laws of nature require the obliteration of the unfit, and human life is valuable only when it is of use to the community or race."
 |
| "You are bearing this too". Courtesy of H. E. A. R. T. |
"The demand that defective people be prevented from propagating equally defective offspring is a demand of the clearest reason and if systematically executed represents the most humane act of mankind. It will spare millions of unfortunates undeserved sufferings, and consequently will lead to a rising improvement of health as a whole."
He
also references the United States frequently, including his his
admiration of restricting immigration. His keen interest in American
eugenics legislation is reflected in this comment to a comrade;
In 1934, the superintendent of Virgina's Western State Hospital complained in the local paper "The Germans are beating us at their own game". For years, Nazi doctors would continue to routinely consult with eugenicists across America.
Extermination and Aktion T4
The first incidence of state performed euthanasia in Germany was known as the "Child K" case. Hitler was approached by the parents of a "deformed" child and asked his permission to allow the child to be put to death. After consulting with his personal physician and chancellor, Hitler granted the child's doctor the ability to euthanize the child.
By August 18th 1939, Hitler had created the Reich
Committee for the Scientific Registering of Serious Hereditary and
Congenital Illnesses (Reichsausschuss zur wissenschaftlichen Erfassung erb- und anlagebedingter schwerer Leiden)
which required mandatory registration of all births of developmentally
delayed and handicapped children by doctors and midwives. Children up
to three years of age had to be reported to the offices of the Reich
Health Ministry. Code named Aktion T4, Hitler ordered the "mercy killing" of all deemed "life unworthy of life"; this plan focused initially on newborns and young children. The program was managed by Hitler's personal physician, Karl Brandt and the chief of Hitler's private chancellery, Philipp Bouler
(the same two whose counsel he sought with Child K). To be included in
this program were those with "idiocy and mongolism" (Down syndrome),
those with blindness and deafness, microcephaly, hydrocephalus, absence
of limbs, mid line defects of the head and spine and paralysis (such as
cerebral palsy). The decision to end a child's life was based on the
results of a questionnaire. No medical examination took place or
records were consulted. Three "medical experts" placed a red + or a
blue - on a form marked "treatment". A minus sign represented a
decision by an "expert" to not kill the child. Three plus signs meant
the issue of a euthanasia warrant and transfer to a "Children's
Specialty Department". A unanimous decision was required; in the event
of a split decision, the child was "observed" for a period of time and
another attempt would be made to achieve a consensus.
Adolf Hitler came to power on January 30, 1933. For the first 10 years of the 12 year Reich, eugenicists welcomed his proposed fulfillment of their tenets of identification, segregation, sterilization, eugenic courts and euthanasia. In July of 1933, Germany passed the "Law for the Prevention of Heriditarily Diseased Offspring". This law provided legal grounds for the sterilization of people deemed by a court hearing to be "unfit". This law provided that any person with a hereditary disease could be sterilized if there was a high probability of it being passed on to future generations. Those listed included "Congenital Mental Deficiency" (such as Down syndrome), schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, epilepsy, Huntington's chorea, blindness, deafness, any severe deformity and those with severe alcoholism. In the general public, the notion of the "useless eater" was perpetuated."...it is possible to a large extent to prevent unhealthy and severely handicapped beings from coming into the world. I have studied with interest the laws of several American states concerning prevention of reproduction by people whose progeny would, in all probability, be of no value or be injurious to the racial stock."
Nazi Eugenics propaganda poster from 1939,
stating "We Do Not Stand Alone"
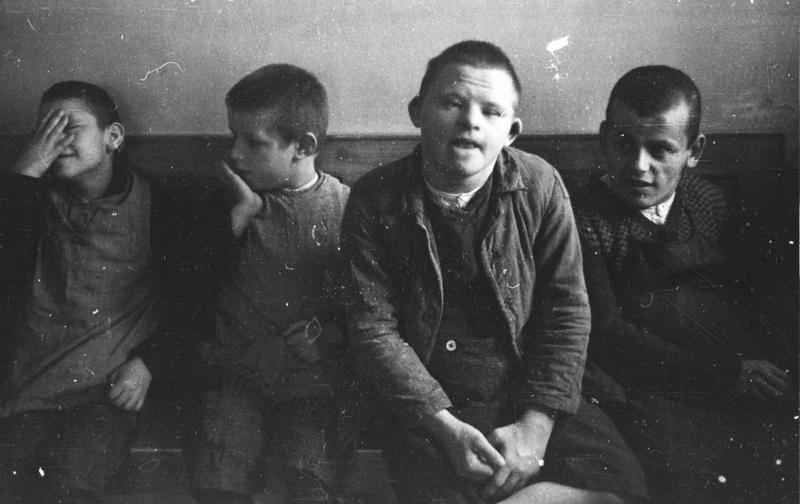 |
| Children at the Schönbrunn Psychiatric Hospital, 1934. (Bundesarchiv, Bild 152-04-28 / Friedrich Franz Bauer / CC-BY-SA\) |
Extermination and Aktion T4
The first incidence of state performed euthanasia in Germany was known as the "Child K" case. Hitler was approached by the parents of a "deformed" child and asked his permission to allow the child to be put to death. After consulting with his personal physician and chancellor, Hitler granted the child's doctor the ability to euthanize the child.
 |
| This poster proclaims “Sterilization is liberation, not a punishment.” and asks “Who would want to be responsible for this?” and features three children with disabilities. Photo courtesy of Calvin College |
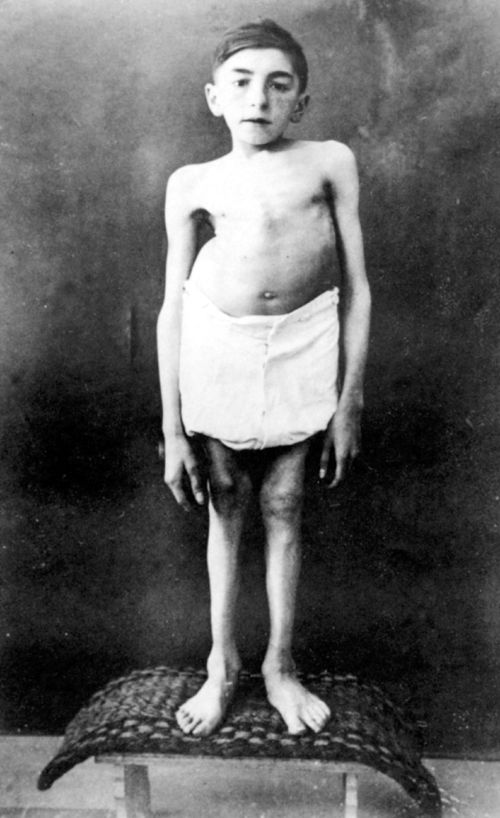
|
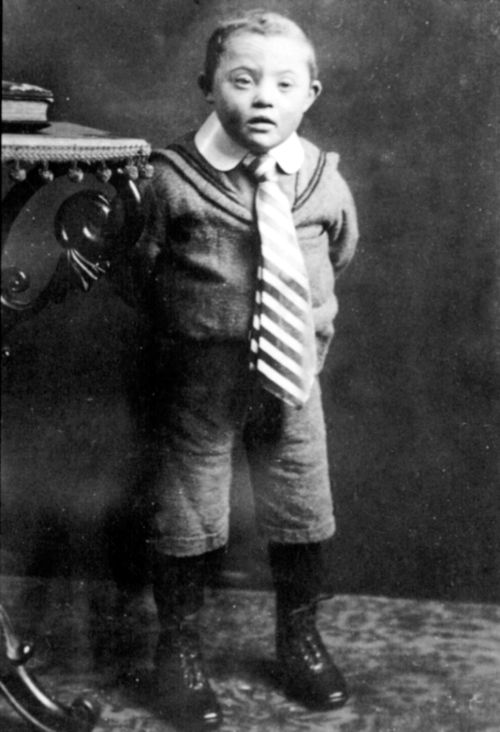

|
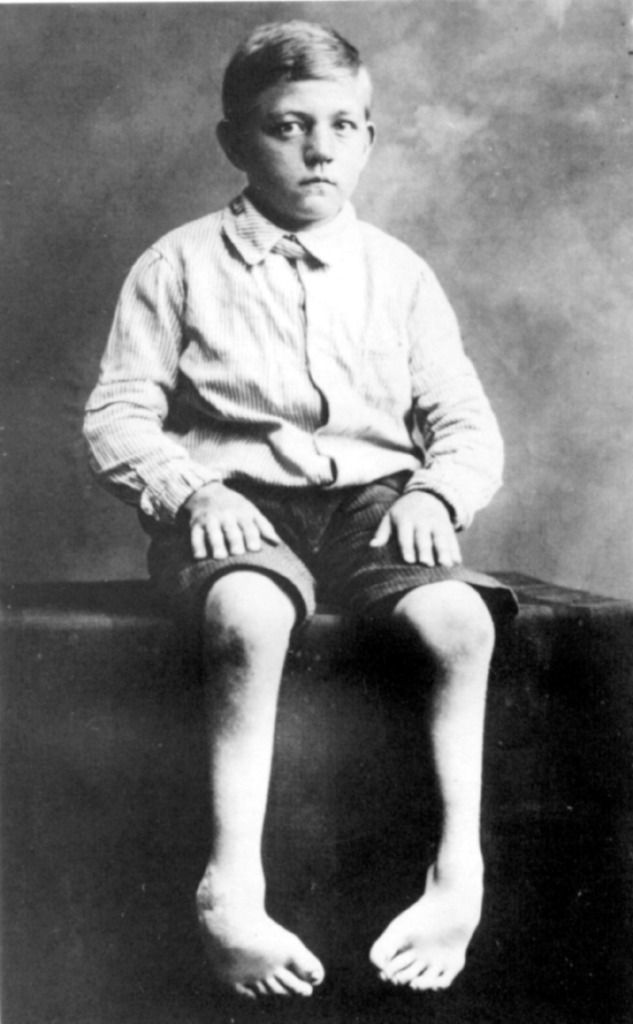

|
| "Life unworthy of life" |
These children were sent to one of six facilities where they were killed by drugs or by starvation. It is belived that 8,000 children were to lose their lives this way. In October of the same year, this decree was extended to include older children and adults. Hitler backdated his declaration to September first and increased the power of
"the authority of certain physicians to be designated by name in such manner that persons who, according to human judgment, are incurable can, upon a most careful diagnosis of their condition of sickness, be accorded a mercy death."This would not only dispose of the "useless eaters" but also free up beds in hospitals for wounded Nazi soldiers. Questionnaires were sent to institutions for the mentally ill, chronically ill and hospitals. Patients were required to be reported if they had schizophrenia, epilepsy, dementia, paralysis, syphillis, developmental delays, encephalitis, neurological conditions, had been in hospital or institutionalized for 5 years or more, was criminally insane, was a foreigner or was Jewish, African-American or Gypsy.
 |
| Tiergartenstraße 4, Courtesy of H. E. A. R. T. |
Six main euthenasia sites were created across Germany and Austria. In January 1940, Brandenburg (near Berlin), Grafeneck (near Stuttgart) and Hartheim (near Linz, Austria) were established; both Brandenburg and Grafeneck ceased functioning (officially) between September and December of the same year. Sonnenstin/Pirna (near Dresden) opened in April of 1940 and Bernberg (near Magdeburg) was established in September. The last to open was Hadamar (near Koblenz) which opened in January the following year (and closed that August). Bernburg ceased operation in April 1943, while Sonnenstein/Pirna ended in August 1943. Hartheim was the last to cease it's operation, which it did officially in December of 1944. The Zwischenanstalten were intermediate stops between the patients institution of origin and the killing centres. They also managed the capacity of the centres and were tasked with 'cover up' for inquiring relatives. It was at Brandenburg, a converted prison, that the first Nazi gas exterminations took place. The T4 victims were gassed in chambers disguised as showers and their remains burned in giant ovens. Families were told that the victims had died of various illnesses including pneumonia or heart failure. They would each recieve an urn contianing mixed ashes. The routine deception and gassing/cremation would be used again, only on a much larger scale.
 |
| The billowing chimney at Hadamar. Ashes with human hair would rain down upon the townspeople. Courtesy of H. E. A. R. T. |
The following three testimonials speak volumes about the killing centres (in this case, Hadamar):
“After doors were closed, the air was sucked out of the gas chamber through a ventilator by the same doctor who carried out the earlier `examination.’ Then for about ten minutes, carbon monoxide was let in [by that doctor] and its effect observed through a small window. As soon as he thought that those shut in had died, he had the gas chamber emptied. First fresh air was introduced through the ventilator, and the gas was forced out. From the beginning of the gassing until the reopening of the gas chamber took about one hour. The corpses that were to be dissected were removed to a special room. However, the great majority of corpses were immediately taken to the ovens and burned there.”
"Through it I saw 40-45 men who were pressed together in the next room and were now slowly dying. Some lay on the ground, others had slumped down, many had their mouths open as if they could not get any more air. The form of death was so painful that one cannot talk of a humane killing, especially since many of the dead men may have had moments of clarity. I watched the process for about 2-3 minutes and then left because I could no longer bear to look and felt sick.”
“Did I ever watch a gassing? Dear God, unfortunately, yes. And it was all due to my curiosity.... Downstairs on the left was a short pathway, and there I looked through the window.... In the chamber there were patients, naked people, some semi-collapsed, others with their mouths terribly wide open, their chests heaving. I saw that, I have never seen anything more gruesome. I turned away, went up the steps, upstairs was a toilet. I vomited everything I had eaten. This pursued me days on end.... Looking into the chamber, I could not imagine that this was completely without pain. Of course, I am a layman and this is just my opinion. A few were lying on the ground. The spines of all the naked people protruded. Some sat on the bench with their mouth wide open, their eyes wide open, and breathing with difficulty.”[Testimonials courtesy of H. E. A. R. T]
A Catholic Bishop in Münster, named Clemens von Galen, delivered a sermon on August 3, 1941 which denounced Aktion T4 as murder. The Nazi party was publicly condemned and the faithful encouraged to withdraw from the party due to their "ungodly" policies. Hitler officially suspended the program 20 days later and in retaliation, beheaded three priests. At that point, over 70 000 lives had been ended. Although it had officially been stopped, it continued quietly in the background, especially in the hospitals of conqured territories and for those that remained in the institutions. Instead of gas, patients were poisoned or starved to death. Physicians were encouraged to err on the side of death when considering such an action.
The gas chambers used in the euthanasia centres were a testing ground; the Nazi party used the Aktion T4 experience to aid in the construction of the death camps in places such as Auschwitz and Treblinka. In fact, many SS officers that participated in the killing centres would go on to command in the camps. Although officially abandoned, Aktion T4 was still considered a "success" and became the opening chapter in what would become the Holocaust.
Meanwhile, in the Allied countries, increasing numbers of institutional workers were being drafted, leaving the already overcrowded conditions even more destitute. Although the horrors of the camps and Aktion T4 were exposed after the war, people continued to be sterilized against their will, long after eugenics was abandoned as a "science". In parts of Canada for example, this would continue well into the 1970's.
[Next time: Abandonment and Abuse]
----------------
Black, Edwin. War Against the Weak: Eugenics and America's Campaign to Create a Master Race. New York: Four Walls Eight Windows, 2003. Print.
"Disability History Exhibit." Disability History Panels. Alaska Department of Health and Social Services, n.d. Web. <http://www.hss.state.ak.us/gcdse/history/HTML_Content_Main.htm>.
Grant, Madison. The Passing of the Great Race or The Racial Bias of European History. New York: Charles Scribner's Sons, 1916. Print.
Hitler, Adolf. Mein Kampf. Germany: Eher Verlag, 1925. Print.
Lifton, Robert J. The Nazi Doctors: Medical Killing and the Psychology of Genocide. New York: Basic, 2000. The Holocaust History Project. Web.
"Nazi Eugenics and Euthanasia." Holocaust Education & Archive Research Team. H. E. A. R. T., 2010. Web. <www.HolocaustResearchProject.org>.
Paralells in Time; A History of Developmental Disabilities, The Minnesota Governor's Council on Developmental Disabilities, 2012.
Popenoe, Paul, and Roswell H. Johnson. Applied Eugenics. New York: MacMillan, 1918. The Project Gutenberg EBook of Applied Eugenics. Project Gutenberg, 17 Oct. 2006. Web. <http://www.gutenberg.org/files/19560/19560-h/19560-h.htm>.
Van Wagenen, Bleeker, "Preliminary Report of the Committee of the Eugenic Section of the American Breeders' Association to Study and to Report on the Best Practical Means for Cutting Off the Defective Germ-Plasm in the Human Population" (2009). College of Law Faculty Publications. Paper 74. <http://digitalarchive.gsu.edu/col_facpub/74>
[Originally appeared on Down Wit Dat]